Networking Devices
1. MODEM:

It is stand for modulation and demodulation.
It is device that modulates the data before data transmission and demodulates the same data with the same rule at the receiving end.
It is used in multimedia networking and internet to transmit the data from copper wire.
There are three types of modulation technique and they are :
a. FSK ( Frequency Shift keying ) or FM (Frequency Modulate )
b. ASK ( Amplitude Shift keying )
c. PSK ( Phase Shift keying ) or PM ( Phase Modulate )
2. Switch/Hub:

It is a common network devices .
It has multiple ports of connecting different computer on the network.
It is used to split the networking media or provide multiple connection.
It operate at physical layer of OSI model.
It accepts data , amplify and then transmit.
3. Bridge:
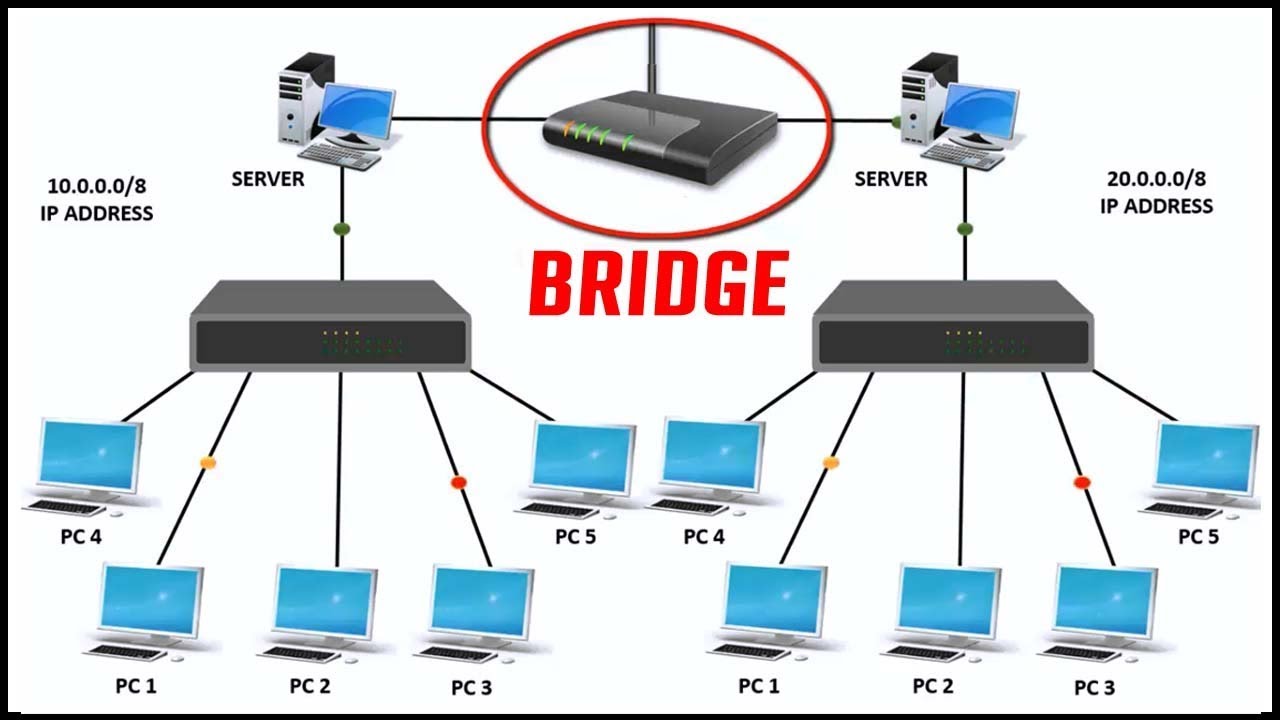
It is a connecting devices that connect two or more hubs.
It is a devices which cannot different network segments and passes data with the same communication protocol.
It is more intelligent then hub because it maintain MAC ( Media Access Control ) address table in it and forward the data by looking into it.
It reduce unnecessary data traffic problem by controlling broad casting.
It operates at layer 2 ( Data Link layer ) of OSI model.
4. Router:

It is an electronic devices that intercept data on a computer network .
It is also used to connect separate network and to access internet.
It is similar to Bridge .
It operates at 3 network layer of OSI model.
5. Repeater:
It operate at layer 1 ( physical layer ) of OSI model.
It receive signal amplifies it and sends it forward.
It increase the distance over which the network can be extended.
OSI ( Open system Interconnection ) Reference Model:
The OSI was released in 1984 AD a standard network model. It decrease how information make its way from application program. Thus media to another application program in another computer.
The OSI reference model is described below:
1. Application layer:
- It is service layer .
- It is closest to the user.
- It provide services to application program.
- It synchronizes the sending & receiving application.
- It determines weather the sufficient resources of the intended communication.
2. Presentation layer:
- It is six layer .
- It ensure that information send by application layer of one system will be readable by the application layer of another system.
- It provide common format for transmitting data across various system. so, that data can be understand .
- It provides facilities to convert meaning to communicating application layer entities.
- It may perform such transformation as recording, decoding, code conversion,comparison and decompression, encryption and decryption on the message data.
3. Session layer:
- It is fifth layer.
- It provides means establishing, maintaining & communicate a dialog or session between two in user end.
- It allows two parties authority is before established a dialog session between them.
- It specifies dialog type one way, two way alternative of two way simultaneous (simplex half duplex , full duplex) an iminated diagnose session. It also provides priority management services which is useful for giving priority to important and time bound message over normal, place important message.
4. Transport layer:
- it is fourth layer.
- it excepts message of any length from the session layer, segment package, submits them into the network layer for transmission and finally re symbol the packet at the destination.
- It includes mechanism for handing and lost and fat of sequence packet.
- The two most popular transport layer protocol are TCP ( Transport Control Protocol) and UDPC ( User Data Protocol) .
5. Network layer :
- It is third layer.
- It is responsible for setting up a logical path between two notes for data communication.
- It is encapsulates frames into packets, which can be transmitted from one node to another node by using a high level addressing & rotating, scheme, of the network.
- The two popular network layer protocol are: X2S and IP ( Internet protocol).
6. Data link layer:
- It is second layer .
- It detect and correct any areas in the transmitted data.
- It partition the raw bit streams into frames so that error detection and correction can be perform independently for each frames.
- It also perform flow control of the frames.
- It is concern with topology.
7. Physical layer:
- It is first layer .
- It creates a physical path in between sender and receiver .
- it is responsibilities for transmitting raw bit streams in between two nodes.
- It also deal with the mechanism details such as size and shape of connecting plugs, the number pins in their plugs and function of each pins etc.




1 Comments
nice work man
ReplyDelete